Less deviation
Characterization of the specific surface area
with the permeation method
Summary
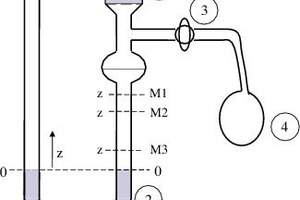
In the scope of this research, the mass specific surface of a standard test substance was determined with Blaine’s permeability method. Test-apparatus-related errors are the result of the inhomogeneity of the material bed caused by compression of the powder, dust generation and consequently the escape of the fines from the particle fraction, and the imprecise guarantee of the porosity of the material bed caused by the pressurization induced by movement of the plunger. With modified test apparatus, deviations in the specific surface of the test substance could be reduced so as to achieve reproducible measuring results.
1 Introduction
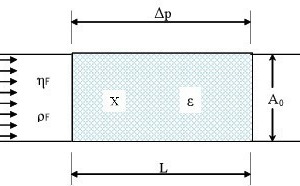
For the characterization of the product properties of a dispersed system or a particle collective, in addition to the particle size distribution, the particle density, the particle shape, the bulk density, etc., the specific surface area is of particular importance. The specific surface area of a discrete-dispersed system can be calculated from the measured size distribution, or measured directly with the sorption or permeability method [1, 2].
In 1943 Blaine presented a test apparatus in which the permeability of a fluid through a particle bed is used to determine the specific...