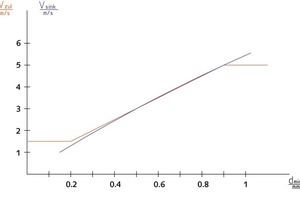
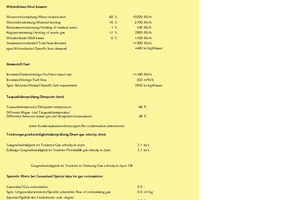
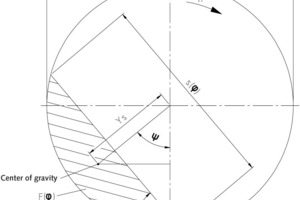
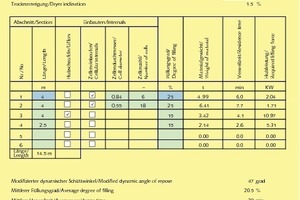
Calculated automatically
Practice-oriented designing for rotary dryers
Abstract
The following article examines a computation programme for the design of rotary dryers. A practicable method for the determination of the necessary dimensions is based on the volumetric drying rate, also referred to as the coefficient of evaporation. All data relevant for process-engineering purposes, such as throughputs, volumetric flows of gas, temperatures, heat demand and power requirement are determined. The computation programme is notable for the fact that practical experience is incorporated for the various process-engineering variants – with the user enjoying extremely large freedom of design, via the input of his or her own empirical data. This computation programme thus permits optimisation and adjustment to the given operational boundary conditions of the user/the designer of rotary dryers.
1 The practicable design of rotary dryers
The drying process occurring in a rotary dryer can be depicted theoretically by means of combination of the differential equations for heat transfer and mass transfer. These equations can be solved using, for example, similarity indices and the coefficients included in them for idealised cases, such as laminar flow, for example. This method is not appropriate for the practical design of rotary dryers, as a result not only of its restricted applicability, but also, and above all, as a result of the unknown similarity indices of the material to be dried...